- neighbor_varThe variable on the other side of the interface.
C++ Type:std::vector<VariableName>
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:The variable on the other side of the interface.
- thicknessThe thin layer thickness
C++ Type:double
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:The thin layer thickness
- variableThe name of the variable that this residual object operates on
C++ Type:NonlinearVariableName
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:The name of the variable that this residual object operates on
ThinLayerHeatTransfer
Model heat transfer across a thin domain with an interface.
Description
This kernel models the heat transfer across a thin domain. The purpose is to model a thin domain with an interface. This will reduce number of mesh elements and avoid high aspect ratio elements within a thin domain. The flux for each side of the gap are defined by the following equations:
where the and indices indicate the primary and neighbor side of the boundary, respectively, is the layer thickness, is a heat source in the layer and , and are thermal conductivity, specific heat and density of the layer.
An example below is used to verify the thin layer heat transfer model. With the interface approach, heat transfer in the thin layer is solved at the interface. Its solution is compared against the case where a thin domain is explicitly represented in the finite element domain.
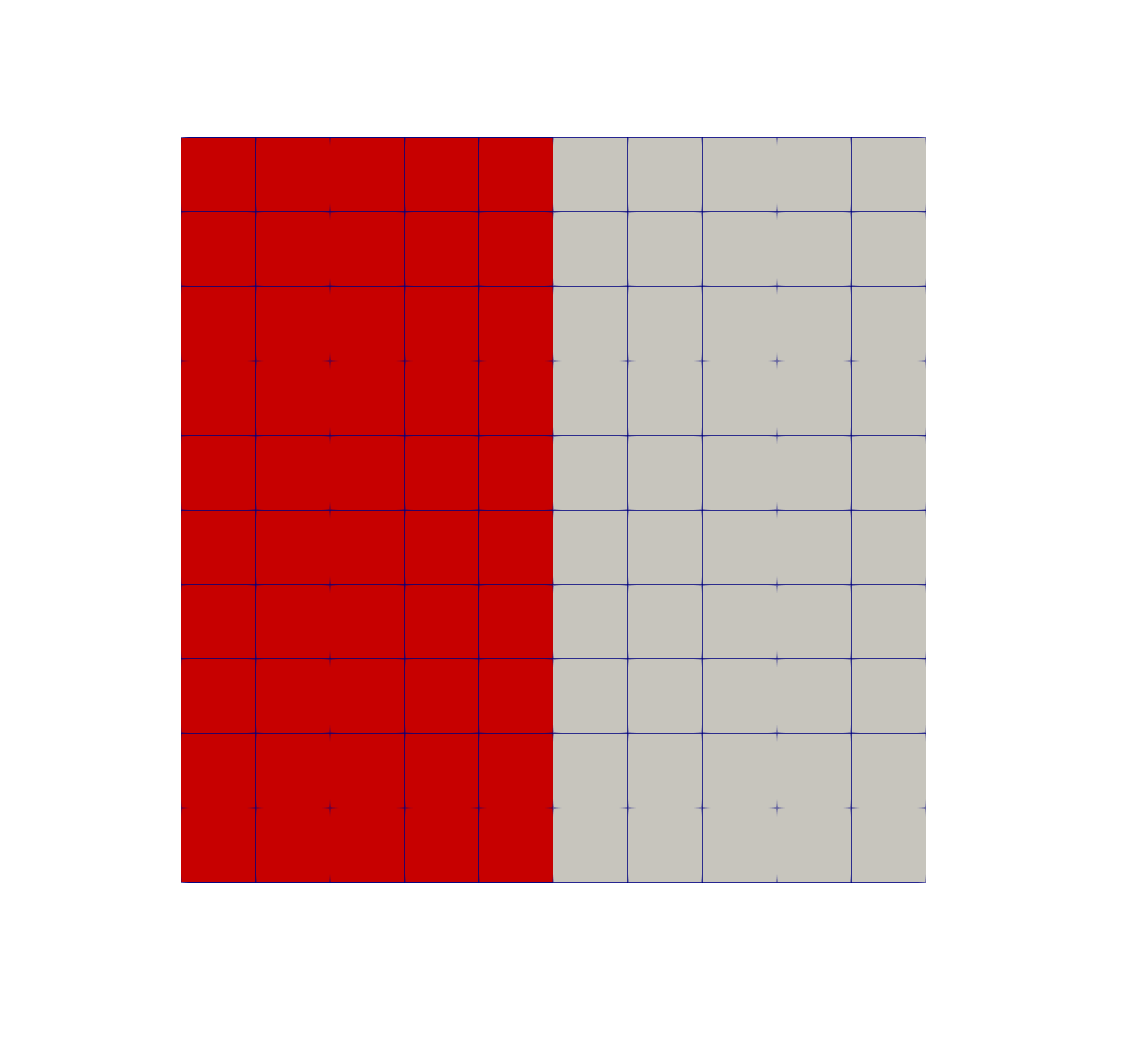
Figure 1: Finite element mesh used for thin layer heat transfer using interfacekernel.
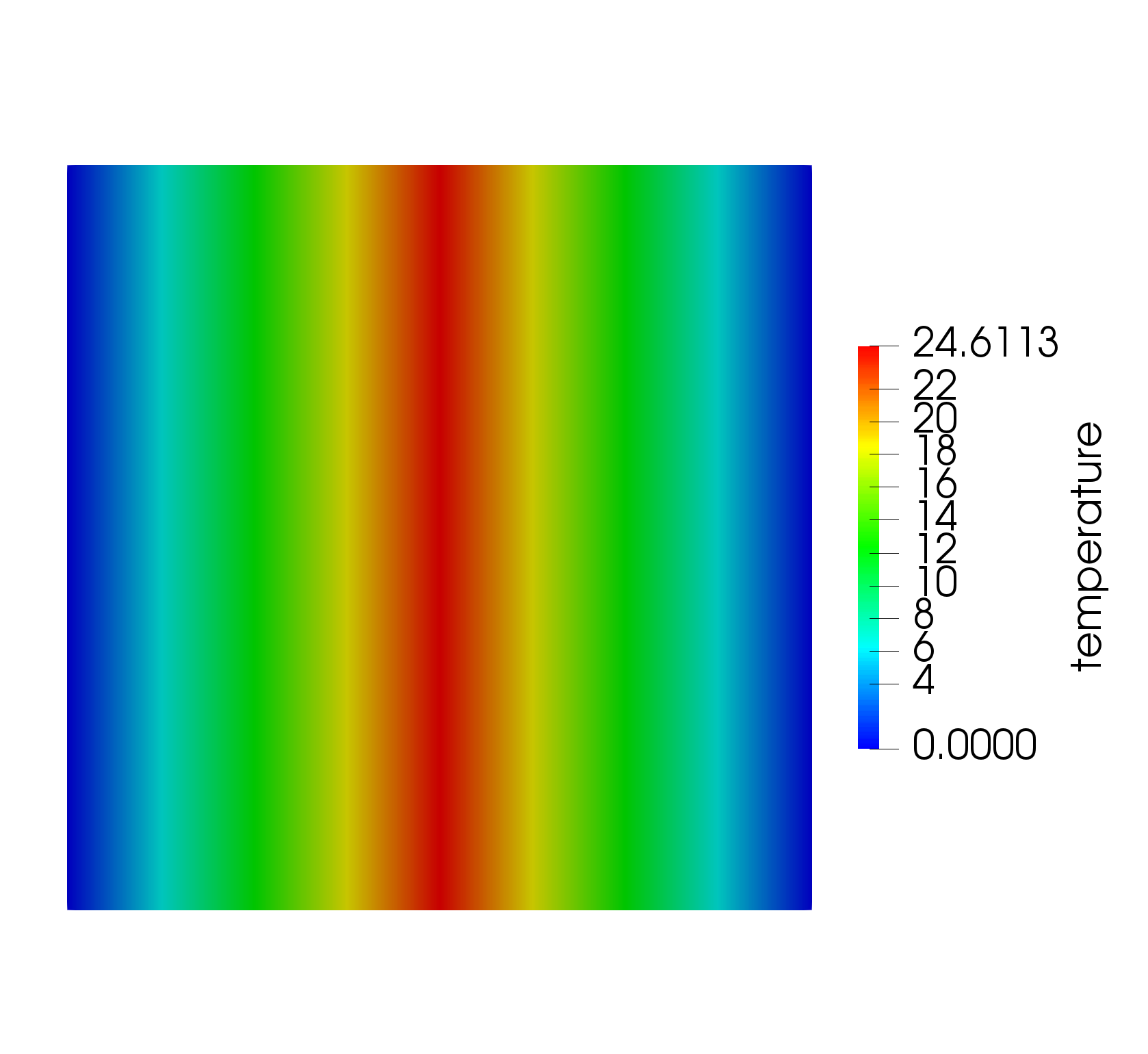
Figure 2: Temperature field for thin layer heat transfer using interfacekernel.
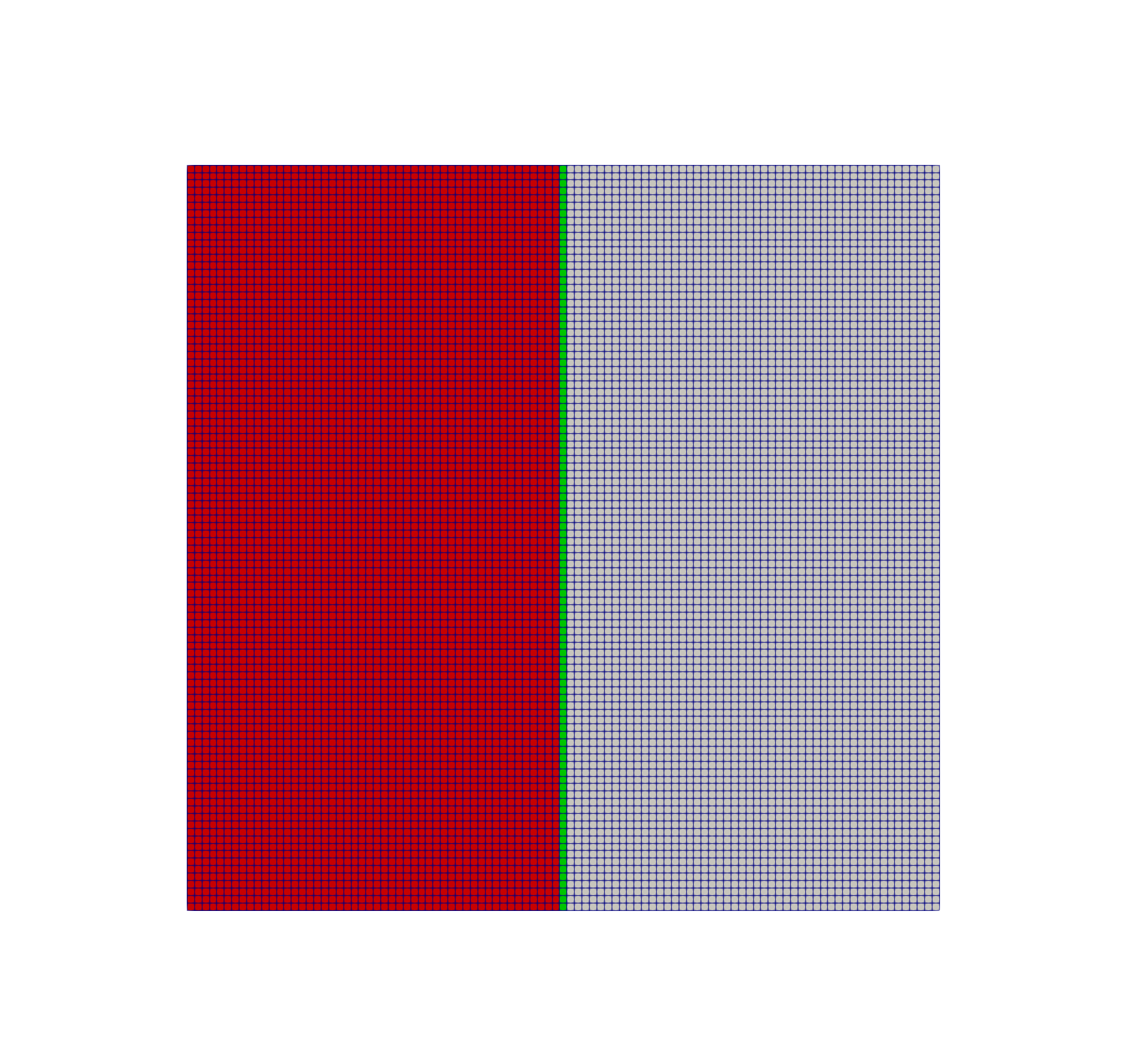
Figure 3: Finite element mesh used for thin layer heat transfer using a thin domain.
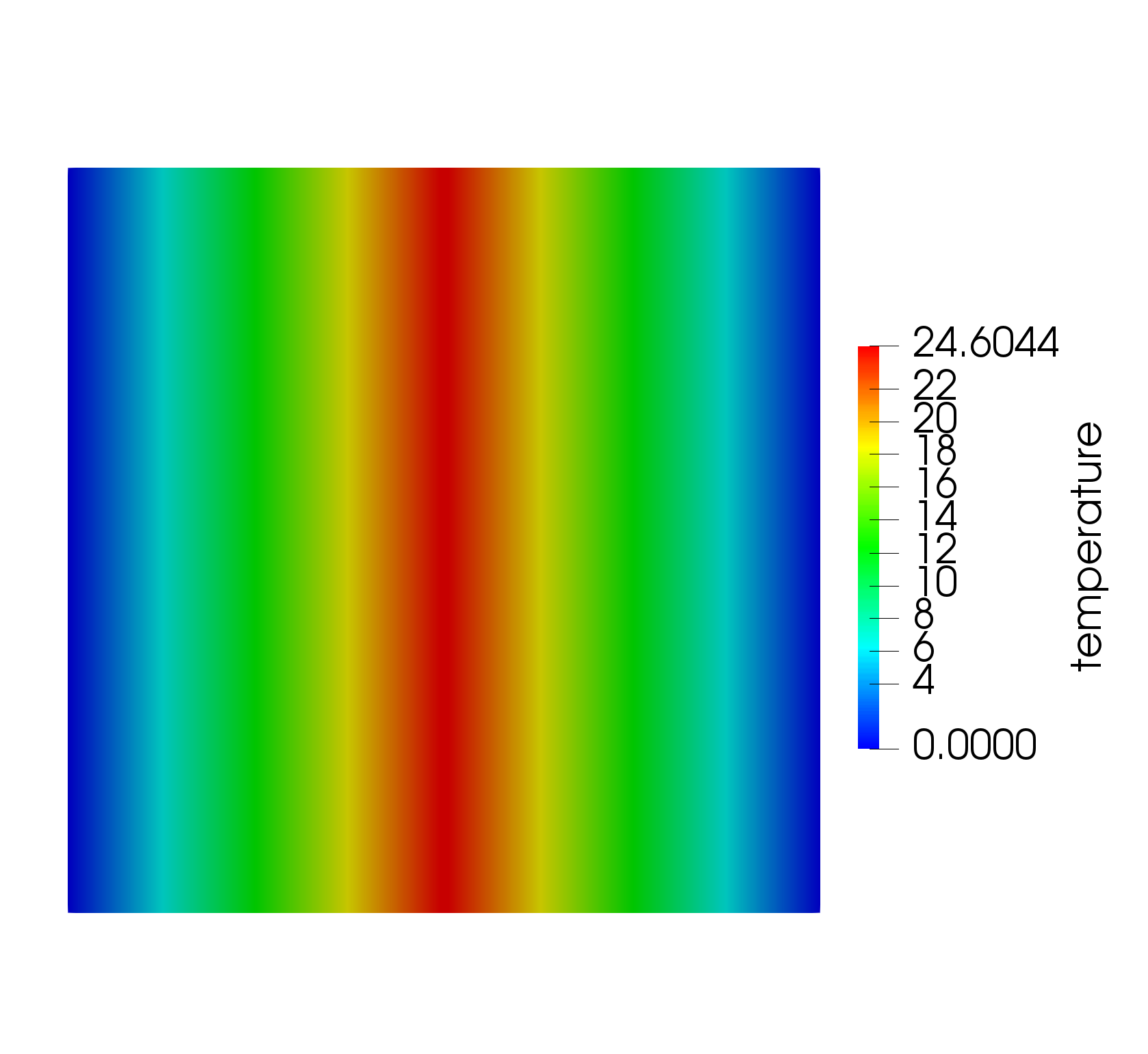
Figure 4: Temperature field for thin layer heat transfer using a thin domain.
Example Input File Syntax
[InterfaceKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/InterfaceKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[thin_layer]
type = ThinLayerHeatTransfer<<<{"description": "Model heat transfer across a thin domain with an interface.", "href": "ThinLayerHeatTransfer.html"}>>>
thermal_conductivity<<<{"description": "Property name of the thermal conductivity"}>>> = thermal_conductivity_layer
specific_heat<<<{"description": "Property name of the specific heat material property of the thin layer"}>>> = specific_heat_layer
density<<<{"description": "Property name of the density material property of the thin layer"}>>> = density_layer
heat_source<<<{"description": "Property name of the heat source material property of the thin layer"}>>> = heat_source_layer
thickness<<<{"description": "The thin layer thickness"}>>> = 0.01
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = temperature
neighbor_var<<<{"description": "The variable on the other side of the interface."}>>> = temperature
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = Block1_Block2
[]
[]Input Parameters
- boundaryThe list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies
C++ Type:std::vector<BoundaryName>
Controllable:No
Description:The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies
- densityProperty name of the density material property of the thin layer
C++ Type:MaterialPropertyName
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:Property name of the density material property of the thin layer
- heat_sourceProperty name of the heat source material property of the thin layer
C++ Type:MaterialPropertyName
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:Property name of the heat source material property of the thin layer
- specific_heatProperty name of the specific heat material property of the thin layer
C++ Type:MaterialPropertyName
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:Property name of the specific heat material property of the thin layer
- thermal_conductivitythermal_conductivityProperty name of the thermal conductivity
Default:thermal_conductivity
C++ Type:MaterialPropertyName
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:Property name of the thermal conductivity
Optional Parameters
- absolute_value_vector_tagsThe tags for the vectors this residual object should fill with the absolute value of the residual contribution
C++ Type:std::vector<TagName>
Controllable:No
Description:The tags for the vectors this residual object should fill with the absolute value of the residual contribution
- extra_matrix_tagsThe extra tags for the matrices this Kernel should fill
C++ Type:std::vector<TagName>
Controllable:No
Description:The extra tags for the matrices this Kernel should fill
- extra_vector_tagsThe extra tags for the vectors this Kernel should fill
C++ Type:std::vector<TagName>
Controllable:No
Description:The extra tags for the vectors this Kernel should fill
- matrix_onlyFalseWhether this object is only doing assembly to matrices (no vectors)
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Whether this object is only doing assembly to matrices (no vectors)
- matrix_tagssystemThe tag for the matrices this Kernel should fill
Default:system
C++ Type:MultiMooseEnum
Controllable:No
Description:The tag for the matrices this Kernel should fill
- vector_tagsnontimeThe tag for the vectors this Kernel should fill
Default:nontime
C++ Type:MultiMooseEnum
Controllable:No
Description:The tag for the vectors this Kernel should fill
Contribution To Tagged Field Data Parameters
- control_tagsAdds user-defined labels for accessing object parameters via control logic.
C++ Type:std::vector<std::string>
Controllable:No
Description:Adds user-defined labels for accessing object parameters via control logic.
- enableTrueSet the enabled status of the MooseObject.
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:Yes
Description:Set the enabled status of the MooseObject.
- implicitTrueDetermines whether this object is calculated using an implicit or explicit form
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Determines whether this object is calculated using an implicit or explicit form
- seed0The seed for the master random number generator
Default:0
C++ Type:unsigned int
Controllable:No
Description:The seed for the master random number generator
- use_displaced_meshFalseWhether or not this object should use the displaced mesh for computation. Note that in the case this is true but no displacements are provided in the Mesh block the undisplaced mesh will still be used.
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Whether or not this object should use the displaced mesh for computation. Note that in the case this is true but no displacements are provided in the Mesh block the undisplaced mesh will still be used.
Advanced Parameters
- diag_save_inThe name of auxiliary variables to save this Kernel's diagonal Jacobian contributions to. Everything about that variable must match everything about this variable (the type, what blocks it's on, etc.)
C++ Type:std::vector<AuxVariableName>
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:The name of auxiliary variables to save this Kernel's diagonal Jacobian contributions to. Everything about that variable must match everything about this variable (the type, what blocks it's on, etc.)
- diag_save_in_var_sideThis parameter must exist if diag_save_in variables are specified and must have the same length as diag_save_in. This vector specifies whether the corresponding aux_var should save-in jacobian contributions from the primary ('p') or secondary side ('s').
C++ Type:MultiMooseEnum
Controllable:No
Description:This parameter must exist if diag_save_in variables are specified and must have the same length as diag_save_in. This vector specifies whether the corresponding aux_var should save-in jacobian contributions from the primary ('p') or secondary side ('s').
- save_inThe name of auxiliary variables to save this Kernel's residual contributions to. Everything about that variable must match everything about this variable (the type, what blocks it's on, etc.)
C++ Type:std::vector<AuxVariableName>
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:The name of auxiliary variables to save this Kernel's residual contributions to. Everything about that variable must match everything about this variable (the type, what blocks it's on, etc.)
- save_in_var_sideThis parameter must exist if save_in variables are specified and must have the same length as save_in. This vector specifies whether the corresponding aux_var should save-in residual contributions from the primary ('p') or secondary side ('s').
C++ Type:MultiMooseEnum
Controllable:No
Description:This parameter must exist if save_in variables are specified and must have the same length as save_in. This vector specifies whether the corresponding aux_var should save-in residual contributions from the primary ('p') or secondary side ('s').
Residual And Jacobian Debug Output Parameters
- prop_getter_suffixAn optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any attempt to retrieve/get material properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
C++ Type:MaterialPropertyName
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:An optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any attempt to retrieve/get material properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
- use_interpolated_stateFalseFor the old and older state use projected material properties interpolated at the quadrature points. To set up projection use the ProjectedStatefulMaterialStorageAction.
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:For the old and older state use projected material properties interpolated at the quadrature points. To set up projection use the ProjectedStatefulMaterialStorageAction.