- phiConcentration variable
C++ Type:std::vector<VariableName>
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:Concentration variable
LinearizedInterfaceFunction
Defines the order parameter substitution for linearized interface phase field models
Overview
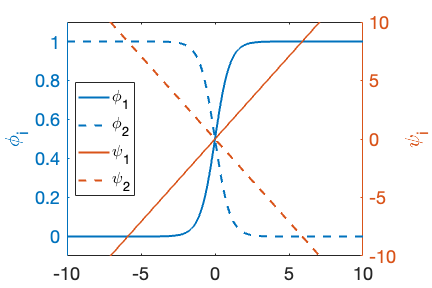
Figure 1: Example of order parameter values (, ) and the linear preconditioning transformed variables (, ),
This material defines the linearized interface substitution defined in Glasner (2001). This substitution converts the profile from a nonlinear shape to a linear shape, as shown in Fig. 1, requiring fewer elements across the interface to accurately resolve.
The transformation implemented in this material is defined as
where is the order parameter and is the transformed variable. The function is implemented using the ExpressionBuilder capability in MOOSE, such that all the derivatives of the function are calculated analytically.
Example Input File Syntax
The material is used via the syntax shown below:
[Materials<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Materials/index.html"}>>>]
[gr0]
type = LinearizedInterfaceFunction<<<{"description": "Defines the order parameter substitution for linearized interface phase field models", "href": "LinearizedInterfaceFunction.html"}>>>
f_name<<<{"description": "Name of the parsed material property"}>>> = gr0
phi<<<{"description": "Concentration variable"}>>> = phi0
[]
[]This material is also generated as part of the automated syntax implemented in GrainGrowthLinearizedInterfaceAction.
Input Parameters
- additional_derivative_symbolsA list of additional (non-variable) symbols (such as material property or postprocessor names) to take derivatives w.r.t.
C++ Type:std::vector<std::string>
Controllable:No
Description:A list of additional (non-variable) symbols (such as material property or postprocessor names) to take derivatives w.r.t.
- blockThe list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied
C++ Type:std::vector<SubdomainName>
Controllable:No
Description:The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied
- boundaryThe list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies
C++ Type:std::vector<BoundaryName>
Controllable:No
Description:The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies
- computeTrueWhen false, MOOSE will not call compute methods on this material. The user must call computeProperties() after retrieving the MaterialBase via MaterialBasePropertyInterface::getMaterialBase(). Non-computed MaterialBases are not sorted for dependencies.
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:When false, MOOSE will not call compute methods on this material. The user must call computeProperties() after retrieving the MaterialBase via MaterialBasePropertyInterface::getMaterialBase(). Non-computed MaterialBases are not sorted for dependencies.
- constant_onNONEWhen ELEMENT, MOOSE will only call computeQpProperties() for the 0th quadrature point, and then copy that value to the other qps.When SUBDOMAIN, MOOSE will only call computeQpProperties() for the 0th quadrature point, and then copy that value to the other qps. Evaluations on element qps will be skipped
Default:NONE
C++ Type:MooseEnum
Controllable:No
Description:When ELEMENT, MOOSE will only call computeQpProperties() for the 0th quadrature point, and then copy that value to the other qps.When SUBDOMAIN, MOOSE will only call computeQpProperties() for the 0th quadrature point, and then copy that value to the other qps. Evaluations on element qps will be skipped
- declare_suffixAn optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any declared properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
C++ Type:MaterialPropertyName
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:An optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any declared properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
- derivative_order3Maximum order of derivatives taken
Default:3
C++ Type:unsigned int
Controllable:No
Description:Maximum order of derivatives taken
- epsilon0Fuzzy comparison tolerance
Default:0
C++ Type:double
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:Fuzzy comparison tolerance
- error_on_missing_material_propertiesTrueThrow an error if any explicitly requested material property does not exist. Otherwise assume it to be zero.
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Throw an error if any explicitly requested material property does not exist. Otherwise assume it to be zero.
- extra_symbolsSpecial symbols, like point coordinates, time, and timestep size.
C++ Type:MultiMooseEnum
Controllable:No
Description:Special symbols, like point coordinates, time, and timestep size.
- property_nameFName of the parsed material property
Default:F
C++ Type:std::string
Controllable:No
Description:Name of the parsed material property
- upstream_materialsList of upstream material properties that must be evaluated when compute=false
C++ Type:std::vector<MaterialName>
Controllable:No
Description:List of upstream material properties that must be evaluated when compute=false
Optional Parameters
- control_tagsAdds user-defined labels for accessing object parameters via control logic.
C++ Type:std::vector<std::string>
Controllable:No
Description:Adds user-defined labels for accessing object parameters via control logic.
- enableTrueSet the enabled status of the MooseObject.
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:Yes
Description:Set the enabled status of the MooseObject.
- implicitTrueDetermines whether this object is calculated using an implicit or explicit form
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Determines whether this object is calculated using an implicit or explicit form
- search_methodnearest_node_connected_sidesChoice of search algorithm. All options begin by finding the nearest node in the primary boundary to a query point in the secondary boundary. In the default nearest_node_connected_sides algorithm, primary boundary elements are searched iff that nearest node is one of their nodes. This is fast to determine via a pregenerated node-to-elem map and is robust on conforming meshes. In the optional all_proximate_sides algorithm, primary boundary elements are searched iff they touch that nearest node, even if they are not topologically connected to it. This is more CPU-intensive but is necessary for robustness on any boundary surfaces which has disconnections (such as Flex IGA meshes) or non-conformity (such as hanging nodes in adaptively h-refined meshes).
Default:nearest_node_connected_sides
C++ Type:MooseEnum
Controllable:No
Description:Choice of search algorithm. All options begin by finding the nearest node in the primary boundary to a query point in the secondary boundary. In the default nearest_node_connected_sides algorithm, primary boundary elements are searched iff that nearest node is one of their nodes. This is fast to determine via a pregenerated node-to-elem map and is robust on conforming meshes. In the optional all_proximate_sides algorithm, primary boundary elements are searched iff they touch that nearest node, even if they are not topologically connected to it. This is more CPU-intensive but is necessary for robustness on any boundary surfaces which has disconnections (such as Flex IGA meshes) or non-conformity (such as hanging nodes in adaptively h-refined meshes).
- seed0The seed for the master random number generator
Default:0
C++ Type:unsigned int
Controllable:No
Description:The seed for the master random number generator
- use_displaced_meshFalseWhether or not this object should use the displaced mesh for computation. Note that in the case this is true but no displacements are provided in the Mesh block the undisplaced mesh will still be used.
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Whether or not this object should use the displaced mesh for computation. Note that in the case this is true but no displacements are provided in the Mesh block the undisplaced mesh will still be used.
Advanced Parameters
- disable_fpoptimizerFalseDisable the function parser algebraic optimizer
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Disable the function parser algebraic optimizer
- enable_ad_cacheTrueEnable caching of function derivatives for faster startup time
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Enable caching of function derivatives for faster startup time
- enable_auto_optimizeTrueEnable automatic immediate optimization of derivatives
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Enable automatic immediate optimization of derivatives
- enable_jitTrueEnable just-in-time compilation of function expressions for faster evaluation
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Enable just-in-time compilation of function expressions for faster evaluation
- evalerror_behaviornanWhat to do if evaluation error occurs. Options are to pass a nan, pass a nan with a warning, throw a error, or throw an exception
Default:nan
C++ Type:MooseEnum
Controllable:No
Description:What to do if evaluation error occurs. Options are to pass a nan, pass a nan with a warning, throw a error, or throw an exception
Parsed Expression Advanced Parameters
- output_propertiesList of material properties, from this material, to output (outputs must also be defined to an output type)
C++ Type:std::vector<std::string>
Controllable:No
Description:List of material properties, from this material, to output (outputs must also be defined to an output type)
- outputsnone Vector of output names where you would like to restrict the output of variables(s) associated with this object
Default:none
C++ Type:std::vector<OutputName>
Controllable:No
Description:Vector of output names where you would like to restrict the output of variables(s) associated with this object
Outputs Parameters
- prop_getter_suffixAn optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any attempt to retrieve/get material properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
C++ Type:MaterialPropertyName
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:An optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any attempt to retrieve/get material properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
- use_interpolated_stateFalseFor the old and older state use projected material properties interpolated at the quadrature points. To set up projection use the ProjectedStatefulMaterialStorageAction.
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:For the old and older state use projected material properties interpolated at the quadrature points. To set up projection use the ProjectedStatefulMaterialStorageAction.
Material Property Retrieval Parameters
References
- Karl Glasner.
Nonlinear preconditioning for diffuse interfaces.
Journal of Computational Physics, 174(2):695–711, 2001.[BibTeX]