Linearized Interface Grain Growth Model
Introduction
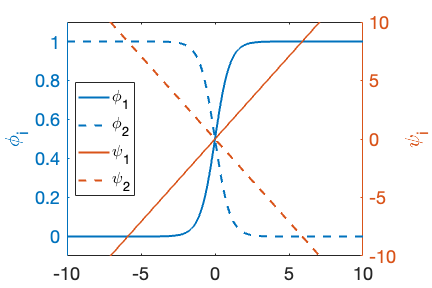
Figure 1: Example of order parameter values (, ) and the linearized interface transformed variables (, ),
In a phase field grain growth model, like that developed by Moelans et al. (2008) and implemented in MOOSE, the order parameters that represent the grains tend to follow a profile across the interface. A fine mesh is required to resolve this highly nonlinear profile, such that at least three elements are typically required across the grain boundaries. This fine mesh required at the grain boundaries makes the computational cost of grain growth simulations high.
The cost of grain growth simulations can be reduced by using a change of variables to linearize the interface profile, sometimes referred to as nonlinear preconditioning and first suggested by Glasner (2001). This change in variables is defined by
where is the original order parameter and is the new variable. While follows a profile across the interface, the new variable is linear across the interface, as illustrated in Figure 1. Due to the linear profile across the interface, a single linear element can resolve the profile without error. This significantly decreases the required resolution, and thus the computational cost.
MOOSE Implementation
Linearized interface has been implemented in the multiphase field grain growth model in MOOSE. The basic model is identical to the standard phase field model in MOOSE, but it solves for the transformed linearized interface variables rather than the standard order parameters. The order parameters are created as AuxVariables, allowing them to be visualized. The grain boundary can be visualized using an AuxVariable equal to , calculated using BndsCalcAux in the usual manner.
The MOOSE objects used in the linearized interface grain growth model are listed, below:
Materials
LinearizedInterfaceFunction - Defines the order parameters from the linear interface variable values at the quadrature points. It uses the ExpressionBuilder so it also calculates the analytical derivatives.
Kernels
ChangedVariableTimeDerivative - Version of the TimeDerivative kernel after a change of variable.
ACGrGrPolyLinearizedInterface - Linearized interface version of the ACGrGrPoly kernel.
ACInterfaceChangedVariable - Version of the ACInterface kernel after a change of variable.
AuxKernels
LinearizedInterfaceAux - Defines AuxVariable values of the order parameters from the nonlinear variable values at the nodes for the linearized interface grain growth model.
Bounded Solve
When solving the linearized interface version of the grain growth model, Gong et al. (2018) and Chadwick and Voorhees (2021) found that the solve is unstable unless bounds are placed on the possible values for the transformed variables. Therefore, upper and lower bounds must be defined in the [Bounds] block for each variable using ConstantBounds. A typical bounds range is . For example:
[Bounds<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Bounds/index.html"}>>>]
[phi0_upper_bound]
type = ConstantBounds<<<{"description": "Provides constant bound of a variable for the PETSc's variational inequalities solver", "href": "../../source/bounds/ConstantBounds.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = bounds_dummy
bounded_variable<<<{"description": "The variable to be bounded"}>>> = phi0
bound_type<<<{"description": "Type of bound. 'upper' refers to the upper bound. 'lower' refers to the lower value."}>>> = upper
bound_value<<<{"description": "The value of bound for the variable"}>>> = 5.0
[]
[phi0_lower_bound]
type = ConstantBounds<<<{"description": "Provides constant bound of a variable for the PETSc's variational inequalities solver", "href": "../../source/bounds/ConstantBounds.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = bounds_dummy
bounded_variable<<<{"description": "The variable to be bounded"}>>> = phi0
bound_type<<<{"description": "Type of bound. 'upper' refers to the upper bound. 'lower' refers to the lower value."}>>> = lower
bound_value<<<{"description": "The value of bound for the variable"}>>> = -5.0
[]
[phi1_upper_bound]
type = ConstantBounds<<<{"description": "Provides constant bound of a variable for the PETSc's variational inequalities solver", "href": "../../source/bounds/ConstantBounds.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = bounds_dummy
bounded_variable<<<{"description": "The variable to be bounded"}>>> = phi1
bound_type<<<{"description": "Type of bound. 'upper' refers to the upper bound. 'lower' refers to the lower value."}>>> = upper
bound_value<<<{"description": "The value of bound for the variable"}>>> = 5.0
[]
[phi1_lower_bound]
type = ConstantBounds<<<{"description": "Provides constant bound of a variable for the PETSc's variational inequalities solver", "href": "../../source/bounds/ConstantBounds.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = bounds_dummy
bounded_variable<<<{"description": "The variable to be bounded"}>>> = phi1
bound_type<<<{"description": "Type of bound. 'upper' refers to the upper bound. 'lower' refers to the lower value."}>>> = lower
bound_value<<<{"description": "The value of bound for the variable"}>>> = -5.0
[]
[]Note that in order for these bounds to have an effect, the user has to specify the PETSc options -snes_type vinewtonssls or -snes_type vinewtonrsls. A warning will be generated if neither options are specified. The PETSc manual pages for the vinewtonssls algorithm can be found here while the manual page for vinewtonrsls can be found here.
These solve options are demonstrated here:
[Executioner<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Executioner/index.html"}>>>]
type = Transient
scheme = bdf2
solve_type = NEWTON
petsc_options_iname = '-pc_type -ksp_type -snes_type'
petsc_options_value = 'bjacobi gmres vinewtonrsls'
dt = 0.1
end_time = 0.6
[]Simplified MOOSE syntax
As with the standard grain growth model in MOOSE, an Action has been created to simplify the input file syntax needed to define a nonlinear preconditioning grain growth model. The GrainGrowthLinearizedInterfaceAction allows the user to specify the number of order parameters to be used in the model and it automatically generates the
Linearized interface variables
AuxVariables and corresponding Auxkernels defining the order parameters
All of the kernels
Material properties defining the order parameters
Upper and lower bounds required for the solve
Auxvariable and kernel defining the grain boundary for visualization
The custom syntax for the linearized interface grain growth model is nearly identical to that for the standard grain growth model, making it simple to switch back and forth between models.
linearized interface Initial Conditions
Initial conditions have been created to transform the IC values for the standard grain growth model to the linearized interface model.
SmoothCircleICLinearizedInterface - Takes the output from the SmoothCircleIC and performs the change in variable. Used to model a shrinking circular grain.
PolycrystalColoringICAction - This custom syntax is used for all polycrystal ICs for both the standard grain growth model and with nolinear preconditioning. The parameter
nonlinear_preconditioning = trueuses the PolycrystalColoringICLinearizedInterface for each variable.
Usage with GrainTracker
GrainTracker, which allows variables to represent multiple grains and remap them to other variables to avoid coalescence, also works with the linearized interface grain growth model. Several changes are needed in its use:
The input parameter
bound_valueshould be set to the value used in the bounded solve. This will switch the variable value when a grain is remapped to -bound_value, erasing the grain from the original variable. This is the same parameter used in GrainGrowthLinearizedInterfaceAction and in the linearized interface ICs, so that it can be set for all of the objects from the GlobalParams block.The
thresholdparameter must be changed to be slightly above the value of the lower bound (-bound_value). It is recommended to use -bound_value+ 2*bound_value/10.
The modified syntax is illustrated here:
[GlobalParams<<<{"href": "../../syntax/GlobalParams/index.html"}>>>]
# Parameters used by several kernels that are defined globally to simplify input file
op_num = 8 # Number of order parameters used
var_name_base = psi # Base name of grains
bound_value = 5 # +/- bound value
[][UserObjects<<<{"href": "../../syntax/UserObjects/index.html"}>>>]
[grain_tracker]
type = GrainTracker<<<{"description": "Grain Tracker object for running reduced order parameter simulations without grain coalescence.", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/GrainTracker.html"}>>>
threshold<<<{"description": "The threshold value for which a new feature may be started"}>>> = -4
[]
[]Example Input Files
An example input file for a polycrystal simulation using the linearized interface grain growth model is available:
[GlobalParams<<<{"href": "../../syntax/GlobalParams/index.html"}>>>]
bound_value = 5.0
op_num = 8
var_name_base = phi
[]
[Mesh<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Mesh/index.html"}>>>]
type = GeneratedMesh
dim = 2
xmax = 1000
ymax = 1000
nx = 100
ny = 100
uniform_refine<<<{"description": "Specify the level of uniform refinement applied to the initial mesh"}>>> = 1
[]
[Modules<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Modules/index.html"}>>>]
[PhaseField<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Modules/PhaseField/index.html"}>>>]
[GrainGrowthLinearizedInterface<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Modules/PhaseField/GrainGrowthLinearizedInterface/index.html"}>>>]
op_name_base<<<{"description": "specifies the base name of the dependent order parameters"}>>> = gr
mobility<<<{"description": "The isotropic mobility used with the kernels"}>>> = L
kappa<<<{"description": "The kappa used with the kernels"}>>> = kappa_op
[]
[]
[]
[ICs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/ICs/index.html"}>>>]
[PolycrystalICs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/ICs/PolycrystalICs/index.html"}>>>]
[PolycrystalColoringIC<<<{"href": "../../syntax/ICs/PolycrystalICs/PolycrystalColoringIC/index.html"}>>>]
polycrystal_ic_uo<<<{"description": "Optional: TODO"}>>> = RandomVoronoi
nonlinear_preconditioning = true
[]
[]
[]
[UserObjects<<<{"href": "../../syntax/UserObjects/index.html"}>>>]
[RandomVoronoi]
type = PolycrystalVoronoi<<<{"description": "Random Voronoi tessellation polycrystal (used by PolycrystalVoronoiAction)", "href": "../../source/userobjects/PolycrystalVoronoi.html"}>>>
grain_num<<<{"description": "Number of grains being represented by the order parameters"}>>> = 60
int_width<<<{"description": "Width of diffuse interfaces"}>>> = 10
rand_seed<<<{"description": "The random seed"}>>> = 103838
[]
[grain_tracker]
type = GrainTracker<<<{"description": "Grain Tracker object for running reduced order parameter simulations without grain coalescence.", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/GrainTracker.html"}>>>
threshold<<<{"description": "The threshold value for which a new feature may be started"}>>> = -4.0
compute_halo_maps<<<{"description": "Instruct the Postprocessor to communicate proper halo information to all ranks"}>>> = true # Only necessary for displaying HALOS
[]
[]
[AuxVariables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/AuxVariables/index.html"}>>>]
[unique_grains]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = CONSTANT
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = MONOMIAL
[]
[var_indices]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = CONSTANT
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = MONOMIAL
[]
[halos]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = CONSTANT
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = MONOMIAL
[]
[]
[AuxKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/AuxKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[unique_grains]
type = FeatureFloodCountAux<<<{"description": "Feature detection by connectivity analysis", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/FeatureFloodCountAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = unique_grains
flood_counter<<<{"description": "The FeatureFloodCount UserObject to get values from."}>>> = grain_tracker
field_display<<<{"description": "Determines how the auxilary field should be colored. (UNIQUE_REGION and VARIABLE_COLORING are nodal, CENTROID is elemental, default: UNIQUE_REGION)"}>>> = UNIQUE_REGION
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = 'initial timestep_end'
[]
[var_indices]
type = FeatureFloodCountAux<<<{"description": "Feature detection by connectivity analysis", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/FeatureFloodCountAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = var_indices
flood_counter<<<{"description": "The FeatureFloodCount UserObject to get values from."}>>> = grain_tracker
field_display<<<{"description": "Determines how the auxilary field should be colored. (UNIQUE_REGION and VARIABLE_COLORING are nodal, CENTROID is elemental, default: UNIQUE_REGION)"}>>> = VARIABLE_COLORING
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = 'initial timestep_end'
[]
[halos]
type = FeatureFloodCountAux<<<{"description": "Feature detection by connectivity analysis", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/FeatureFloodCountAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = halos
flood_counter<<<{"description": "The FeatureFloodCount UserObject to get values from."}>>> = grain_tracker
field_display<<<{"description": "Determines how the auxilary field should be colored. (UNIQUE_REGION and VARIABLE_COLORING are nodal, CENTROID is elemental, default: UNIQUE_REGION)"}>>> = HALOS
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = 'initial timestep_end'
[]
[]
[Materials<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Materials/index.html"}>>>]
[properties]
type = GenericConstantMaterial<<<{"description": "Declares material properties based on names and values prescribed by input parameters.", "href": "../../source/materials/GenericConstantMaterial.html"}>>>
prop_names<<<{"description": "The names of the properties this material will have"}>>> = 'gbmob gbenergy gbwidth gamma_asymm'
prop_values<<<{"description": "The values associated with the named properties"}>>> = '100 6 10 1.5'
[]
[kappa_op]
type = ParsedMaterial<<<{"description": "Parsed expression Material.", "href": "../../source/materials/ParsedMaterial.html"}>>>
material_property_names<<<{"description": "Vector of material properties used in the parsed function"}>>> = 'gbenergy gbwidth'
property_name<<<{"description": "Name of the parsed material property"}>>> = kappa_op
expression<<<{"description": "Parsed function (see FParser) expression for the parsed material"}>>> = '3/4*gbenergy*gbwidth'
[]
[L]
type = ParsedMaterial<<<{"description": "Parsed expression Material.", "href": "../../source/materials/ParsedMaterial.html"}>>>
material_property_names<<<{"description": "Vector of material properties used in the parsed function"}>>> = 'gbmob gbwidth'
property_name<<<{"description": "Name of the parsed material property"}>>> = L
expression<<<{"description": "Parsed function (see FParser) expression for the parsed material"}>>> = '4/3*gbmob/gbwidth'
[]
[mu]
type = ParsedMaterial<<<{"description": "Parsed expression Material.", "href": "../../source/materials/ParsedMaterial.html"}>>>
material_property_names<<<{"description": "Vector of material properties used in the parsed function"}>>> = 'gbenergy gbwidth'
property_name<<<{"description": "Name of the parsed material property"}>>> = mu
expression<<<{"description": "Parsed function (see FParser) expression for the parsed material"}>>> = '6*gbenergy/gbwidth'
[]
[]
[Postprocessors<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Postprocessors/index.html"}>>>]
[dt]
type = TimestepSize<<<{"description": "Reports the timestep size", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/TimestepSize.html"}>>>
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = 'initial TIMESTEP_END'
[]
[]
[BCs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/BCs/index.html"}>>>]
[Periodic<<<{"href": "../../syntax/BCs/Periodic/index.html"}>>>]
[All]
auto_direction<<<{"description": "If using a generated mesh, you can specify just the dimension(s) you want to mark as periodic"}>>> = 'x y'
[]
[]
[]
[Executioner<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Executioner/index.html"}>>>]
type = Transient
scheme = bdf2
solve_type = PJFNK
petsc_options_iname = '-pc_type -pc_hypre_type -snes_type'
petsc_options_value = 'hypre boomeramg vinewtonrsls'
l_tol = 1e-4
nl_max_its = 10
l_max_its = 45
[TimeStepper<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Executioner/TimeStepper/index.html"}>>>]
type = IterationAdaptiveDT
dt = 0.02
optimal_iterations = 6
[]
end_time = 30
[]
[Outputs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Outputs/index.html"}>>>]
exodus<<<{"description": "Output the results using the default settings for Exodus output."}>>> = true
perf_graph<<<{"description": "Enable printing of the performance graph to the screen (Console)"}>>> = true
[]The linearized interface tests also serve as good examples for how to use the capability.
The evolution of a shrinking circular grain is illustrated here:
[Mesh<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Mesh/index.html"}>>>]
type = GeneratedMesh
dim = 2
xmax = 50
ymax = 50
nx = 10
ny = 10
[]
[Variables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Variables/index.html"}>>>]
[phi0]
[]
[phi1]
[]
[]
[AuxVariables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/AuxVariables/index.html"}>>>]
[gr0_aux]
[]
[gr1_aux]
[]
[bounds_dummy]
[]
[]
[AuxKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/AuxKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[gr0]
type = LinearizedInterfaceAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the order parameter from the linearized interface function", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/LinearizedInterfaceAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = gr0_aux
nonlinear_variable<<<{"description": "The variable used in the linearized interface function"}>>> = phi0
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = 'INITIAL TIMESTEP_END'
[]
[gr1]
type = LinearizedInterfaceAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the order parameter from the linearized interface function", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/LinearizedInterfaceAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = gr1_aux
nonlinear_variable<<<{"description": "The variable used in the linearized interface function"}>>> = phi1
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = 'INITIAL TIMESTEP_END'
[]
[]
[ICs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/ICs/index.html"}>>>]
[phi0_IC]
type = SmoothCircleICLinearizedInterface<<<{"description": "Circle with a smooth interface transformed using the linearized interface function", "href": "../../source/ics/SmoothCircleICLinearizedInterface.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The variable this initial condition is supposed to provide values for."}>>> = phi0
invalue<<<{"description": "The variable value inside the circle"}>>> = 1.0
outvalue<<<{"description": "The variable value outside the circle"}>>> = 0.0
bound_value<<<{"description": "Bound value used to keep variable between +/-bound. Must be positive."}>>> = 5.0
radius<<<{"description": "The radius of a circle"}>>> = 30
int_width<<<{"description": "The interfacial width of the void surface. Defaults to sharp interface"}>>> = 10
x1<<<{"description": "The x coordinate of the circle center"}>>> = 0.0
y1<<<{"description": "The y coordinate of the circle center"}>>> = 0.0
profile<<<{"description": "Functional dependence for the interface profile"}>>> = TANH
[]
[phi1_IC]
type = SmoothCircleICLinearizedInterface<<<{"description": "Circle with a smooth interface transformed using the linearized interface function", "href": "../../source/ics/SmoothCircleICLinearizedInterface.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The variable this initial condition is supposed to provide values for."}>>> = phi1
invalue<<<{"description": "The variable value inside the circle"}>>> = 0.0
outvalue<<<{"description": "The variable value outside the circle"}>>> = 1.0
bound_value<<<{"description": "Bound value used to keep variable between +/-bound. Must be positive."}>>> = 5.0
radius<<<{"description": "The radius of a circle"}>>> = 30
int_width<<<{"description": "The interfacial width of the void surface. Defaults to sharp interface"}>>> = 10
x1<<<{"description": "The x coordinate of the circle center"}>>> = 0.0
y1<<<{"description": "The y coordinate of the circle center"}>>> = 0.0
profile<<<{"description": "Functional dependence for the interface profile"}>>> = TANH
[]
[]
[Kernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Kernels/index.html"}>>>]
#phi0 Kernels
[phi0_dot]
type = ChangedVariableTimeDerivative<<<{"description": "A modified time derivative Kernel that multiplies the time derivative bythe derivative of the nonlinear preconditioning function", "href": "../../source/kernels/ChangedVariableTimeDerivative.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = phi0
order_parameter<<<{"description": "Order parameter material defining the nonlinear preconditioning function"}>>> = gr0
[]
[phi0_ACInt]
type = ACInterfaceChangedVariable<<<{"description": "Gradient energy Allen-Cahn Kernel using a change of variable", "href": "../../source/kernels/ACInterfaceChangedVariable.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = phi0
kappa_name<<<{"description": "The kappa used with the kernel"}>>> = kappa_op
mob_name<<<{"description": "The mobility used with the kernel"}>>> = L
order_parameter<<<{"description": "Order parameter material defnining the change of variable function"}>>> = gr0
[]
[gr0_AC]
type = ACGrGrPolyLinearizedInterface<<<{"description": "Grain growth model Allen-Cahn Kernel with linearized interface variable transformation", "href": "../../source/kernels/ACGrGrPolyLinearizedInterface.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = phi0
mob_name<<<{"description": "The mobility used with the kernel"}>>> = L
this_op<<<{"description": "The material property defining the order parameter for this variable"}>>> = gr0
other_ops<<<{"description": "List of properties defining the order parameters for the variables in v"}>>> = gr1
v<<<{"description": "Array of coupled order parameter names for other order parameters"}>>> = phi1
[]
#phi1 Kernels
[phi1_dot]
type = ChangedVariableTimeDerivative<<<{"description": "A modified time derivative Kernel that multiplies the time derivative bythe derivative of the nonlinear preconditioning function", "href": "../../source/kernels/ChangedVariableTimeDerivative.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = phi1
order_parameter<<<{"description": "Order parameter material defining the nonlinear preconditioning function"}>>> = gr1
[]
[phi1_ACInt]
type = ACInterfaceChangedVariable<<<{"description": "Gradient energy Allen-Cahn Kernel using a change of variable", "href": "../../source/kernels/ACInterfaceChangedVariable.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = phi1
kappa_name<<<{"description": "The kappa used with the kernel"}>>> = kappa_op
mob_name<<<{"description": "The mobility used with the kernel"}>>> = L
order_parameter<<<{"description": "Order parameter material defnining the change of variable function"}>>> = gr1
[]
[gr1_AC]
type = ACGrGrPolyLinearizedInterface<<<{"description": "Grain growth model Allen-Cahn Kernel with linearized interface variable transformation", "href": "../../source/kernels/ACGrGrPolyLinearizedInterface.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = phi1
mob_name<<<{"description": "The mobility used with the kernel"}>>> = L
this_op<<<{"description": "The material property defining the order parameter for this variable"}>>> = gr1
other_ops<<<{"description": "List of properties defining the order parameters for the variables in v"}>>> = gr0
v<<<{"description": "Array of coupled order parameter names for other order parameters"}>>> = phi0
[]
[]
[Materials<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Materials/index.html"}>>>]
[gr0]
type = LinearizedInterfaceFunction<<<{"description": "Defines the order parameter substitution for linearized interface phase field models", "href": "../../source/materials/LinearizedInterfaceFunction.html"}>>>
f_name<<<{"description": "Name of the parsed material property"}>>> = gr0
phi<<<{"description": "Concentration variable"}>>> = phi0
[]
[gr1]
type = LinearizedInterfaceFunction<<<{"description": "Defines the order parameter substitution for linearized interface phase field models", "href": "../../source/materials/LinearizedInterfaceFunction.html"}>>>
f_name<<<{"description": "Name of the parsed material property"}>>> = gr1
phi<<<{"description": "Concentration variable"}>>> = phi1
[]
[GBEovlution]
type = GBEvolution<<<{"description": "Computes necessary material properties for the isotropic grain growth model", "href": "../../source/materials/GBEvolution.html"}>>>
GBenergy<<<{"description": "Grain boundary energy in J/m^2"}>>> = 0.97
GBMobility<<<{"description": "GB mobility input in m^4/(J*s), that overrides the temperature dependent calculation"}>>> = 0.6e-6
T<<<{"description": "Temperature in Kelvin"}>>> = 300
wGB<<<{"description": "Diffuse GB width in the length scale of the model"}>>> = 10
[]
[]
[Bounds<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Bounds/index.html"}>>>]
[phi0_upper_bound]
type = ConstantBounds<<<{"description": "Provides constant bound of a variable for the PETSc's variational inequalities solver", "href": "../../source/bounds/ConstantBounds.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = bounds_dummy
bounded_variable<<<{"description": "The variable to be bounded"}>>> = phi0
bound_type<<<{"description": "Type of bound. 'upper' refers to the upper bound. 'lower' refers to the lower value."}>>> = upper
bound_value<<<{"description": "The value of bound for the variable"}>>> = 5.0
[]
[phi0_lower_bound]
type = ConstantBounds<<<{"description": "Provides constant bound of a variable for the PETSc's variational inequalities solver", "href": "../../source/bounds/ConstantBounds.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = bounds_dummy
bounded_variable<<<{"description": "The variable to be bounded"}>>> = phi0
bound_type<<<{"description": "Type of bound. 'upper' refers to the upper bound. 'lower' refers to the lower value."}>>> = lower
bound_value<<<{"description": "The value of bound for the variable"}>>> = -5.0
[]
[phi1_upper_bound]
type = ConstantBounds<<<{"description": "Provides constant bound of a variable for the PETSc's variational inequalities solver", "href": "../../source/bounds/ConstantBounds.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = bounds_dummy
bounded_variable<<<{"description": "The variable to be bounded"}>>> = phi1
bound_type<<<{"description": "Type of bound. 'upper' refers to the upper bound. 'lower' refers to the lower value."}>>> = upper
bound_value<<<{"description": "The value of bound for the variable"}>>> = 5.0
[]
[phi1_lower_bound]
type = ConstantBounds<<<{"description": "Provides constant bound of a variable for the PETSc's variational inequalities solver", "href": "../../source/bounds/ConstantBounds.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = bounds_dummy
bounded_variable<<<{"description": "The variable to be bounded"}>>> = phi1
bound_type<<<{"description": "Type of bound. 'upper' refers to the upper bound. 'lower' refers to the lower value."}>>> = lower
bound_value<<<{"description": "The value of bound for the variable"}>>> = -5.0
[]
[]
[Postprocessors<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Postprocessors/index.html"}>>>]
[grain_area_mat]
type = ElementIntegralMaterialProperty<<<{"description": "Compute the integral of the material property over the domain", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/ElementIntegralMaterialProperty.html"}>>>
mat_prop<<<{"description": "The name of the material property"}>>> = gr0
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = 'initial TIMESTEP_END'
[]
[]
[Executioner<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Executioner/index.html"}>>>]
type = Transient
scheme = bdf2
solve_type = NEWTON
petsc_options_iname = '-pc_type -ksp_type -snes_type'
petsc_options_value = 'bjacobi gmres vinewtonrsls'
dt = 0.1
end_time = 0.6
[]
[Outputs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Outputs/index.html"}>>>]
exodus<<<{"description": "Output the results using the default settings for Exodus output."}>>> = true
[]The same problem but using GrainGrowthLinearizedInterfaceAction is illustrated here:
[GlobalParams<<<{"href": "../../syntax/GlobalParams/index.html"}>>>]
bound_value = 5.0
[]
[Mesh<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Mesh/index.html"}>>>]
type = GeneratedMesh
dim = 2
xmax = 50
ymax = 50
nx = 10
ny = 10
[]
[Modules<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Modules/index.html"}>>>]
[PhaseField<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Modules/PhaseField/index.html"}>>>]
[GrainGrowthLinearizedInterface<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Modules/PhaseField/GrainGrowthLinearizedInterface/index.html"}>>>]
op_num<<<{"description": "specifies the number of order parameters to create"}>>> = 2
var_name_base<<<{"description": "specifies the base name of the variables"}>>> = phi
op_name_base<<<{"description": "specifies the base name of the dependent order parameters"}>>> = gr
mobility<<<{"description": "The isotropic mobility used with the kernels"}>>> = L
kappa<<<{"description": "The kappa used with the kernels"}>>> = kappa_op
[]
[]
[]
[ICs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/ICs/index.html"}>>>]
[phi0_IC]
type = SmoothCircleICLinearizedInterface<<<{"description": "Circle with a smooth interface transformed using the linearized interface function", "href": "../../source/ics/SmoothCircleICLinearizedInterface.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The variable this initial condition is supposed to provide values for."}>>> = phi0
invalue<<<{"description": "The variable value inside the circle"}>>> = 1.0
outvalue<<<{"description": "The variable value outside the circle"}>>> = 0.0
radius<<<{"description": "The radius of a circle"}>>> = 30
int_width<<<{"description": "The interfacial width of the void surface. Defaults to sharp interface"}>>> = 10
x1<<<{"description": "The x coordinate of the circle center"}>>> = 0.0
y1<<<{"description": "The y coordinate of the circle center"}>>> = 0.0
profile<<<{"description": "Functional dependence for the interface profile"}>>> = TANH
[]
[phi1_IC]
type = SmoothCircleICLinearizedInterface<<<{"description": "Circle with a smooth interface transformed using the linearized interface function", "href": "../../source/ics/SmoothCircleICLinearizedInterface.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The variable this initial condition is supposed to provide values for."}>>> = phi1
invalue<<<{"description": "The variable value inside the circle"}>>> = 0.0
outvalue<<<{"description": "The variable value outside the circle"}>>> = 1.0
radius<<<{"description": "The radius of a circle"}>>> = 30
int_width<<<{"description": "The interfacial width of the void surface. Defaults to sharp interface"}>>> = 10
x1<<<{"description": "The x coordinate of the circle center"}>>> = 0.0
y1<<<{"description": "The y coordinate of the circle center"}>>> = 0.0
profile<<<{"description": "Functional dependence for the interface profile"}>>> = TANH
[]
[]
[Materials<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Materials/index.html"}>>>]
[GBEovlution]
type = GBEvolution<<<{"description": "Computes necessary material properties for the isotropic grain growth model", "href": "../../source/materials/GBEvolution.html"}>>>
GBenergy<<<{"description": "Grain boundary energy in J/m^2"}>>> = 0.97
GBMobility<<<{"description": "GB mobility input in m^4/(J*s), that overrides the temperature dependent calculation"}>>> = 0.6e-6
T<<<{"description": "Temperature in Kelvin"}>>> = 300
wGB<<<{"description": "Diffuse GB width in the length scale of the model"}>>> = 10
[]
[]
[Postprocessors<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Postprocessors/index.html"}>>>]
[grain_area_mat]
type = ElementIntegralMaterialProperty<<<{"description": "Compute the integral of the material property over the domain", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/ElementIntegralMaterialProperty.html"}>>>
mat_prop<<<{"description": "The name of the material property"}>>> = gr0
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = 'initial TIMESTEP_END'
[]
[]
[Executioner<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Executioner/index.html"}>>>]
type = Transient
scheme = bdf2
solve_type = NEWTON
petsc_options_iname = '-pc_type -ksp_type -snes_type'
petsc_options_value = 'bjacobi gmres vinewtonrsls'
dt = 0.1
end_time = 0.6
[]
[Outputs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Outputs/index.html"}>>>]
exodus<<<{"description": "Output the results using the default settings for Exodus output."}>>> = true
[]The evolution of a five-grain polycrystal is illustrated here:
[GlobalParams<<<{"href": "../../syntax/GlobalParams/index.html"}>>>]
bound_value = 5.0
op_num = 5
var_name_base = phi
[]
[Mesh<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Mesh/index.html"}>>>]
type = GeneratedMesh
dim = 2
xmax = 100
ymax = 100
nx = 20
ny = 20
[]
[Modules<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Modules/index.html"}>>>]
[PhaseField<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Modules/PhaseField/index.html"}>>>]
[GrainGrowthLinearizedInterface<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Modules/PhaseField/GrainGrowthLinearizedInterface/index.html"}>>>]
op_name_base<<<{"description": "specifies the base name of the dependent order parameters"}>>> = gr
mobility<<<{"description": "The isotropic mobility used with the kernels"}>>> = L
kappa<<<{"description": "The kappa used with the kernels"}>>> = kappa_op
[]
[]
[]
[ICs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/ICs/index.html"}>>>]
[PolycrystalICs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/ICs/PolycrystalICs/index.html"}>>>]
[PolycrystalColoringIC<<<{"href": "../../syntax/ICs/PolycrystalICs/PolycrystalColoringIC/index.html"}>>>]
polycrystal_ic_uo<<<{"description": "Optional: TODO"}>>> = RandomVoronoi
linearized_interface<<<{"description": "Whether to use linearized interface or the standard model"}>>> = true
[]
[]
[]
[UserObjects<<<{"href": "../../syntax/UserObjects/index.html"}>>>]
[RandomVoronoi]
type = PolycrystalVoronoi<<<{"description": "Random Voronoi tessellation polycrystal (used by PolycrystalVoronoiAction)", "href": "../../source/userobjects/PolycrystalVoronoi.html"}>>>
grain_num<<<{"description": "Number of grains being represented by the order parameters"}>>> = 5
int_width<<<{"description": "Width of diffuse interfaces"}>>> = 10
rand_seed<<<{"description": "The random seed"}>>> = 103838
[]
[]
[Materials<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Materials/index.html"}>>>]
[GBEovlution]
type = GBEvolution<<<{"description": "Computes necessary material properties for the isotropic grain growth model", "href": "../../source/materials/GBEvolution.html"}>>>
GBenergy<<<{"description": "Grain boundary energy in J/m^2"}>>> = 0.97
GBMobility<<<{"description": "GB mobility input in m^4/(J*s), that overrides the temperature dependent calculation"}>>> = 0.6e-6
T<<<{"description": "Temperature in Kelvin"}>>> = 300
wGB<<<{"description": "Diffuse GB width in the length scale of the model"}>>> = 10
[]
[]
[Executioner<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Executioner/index.html"}>>>]
type = Transient
scheme = bdf2
solve_type = NEWTON
petsc_options_iname = '-pc_type -ksp_type -snes_type'
petsc_options_value = 'bjacobi gmres vinewtonrsls'
dt = 0.05
num_steps = 1
[]
[Outputs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Outputs/index.html"}>>>]
exodus<<<{"description": "Output the results using the default settings for Exodus output."}>>> = true
[]References
- Alexander F Chadwick and Peter W Voorhees.
The development of grain structure during additive manufacturing.
Acta Materialia, 211:116862, 2021.[BibTeX]
- Karl Glasner.
Nonlinear preconditioning for diffuse interfaces.
Journal of Computational Physics, 174(2):695–711, 2001.[BibTeX]
- Tong Zhao Gong, Yun Chen, Yan Fei Cao, Xiu Hong Kang, and Dian Zhong Li.
Fast simulations of a large number of crystals growth in centimeter-scale during alloy solidification via nonlinearly preconditioned quantitative phase-field formula.
Computational Materials Science, 147:338–352, 2018.[BibTeX]
- N. Moelans, B. Blanpain, and P. Wollants.
Quantitative analysis of grain boundary properties in a generalized phase field model for grain growth in anisotropic systems.
Physical Review B, 78(2):024113, Jul 2008.
URL: http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevB.78.024113 (visited on 2016-06-02), doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.78.024113.[BibTeX]