Initial Conditions
With the phase field method, the initial condition is critical, as it establishes the initial microstructure of the material. MOOSE has a system for creating Initial Conditions (ICs), however there are various initial conditions that have been created as part of the Phase Field Module. The corresponding .C files for each IC can be found in moose/modules/phase_field/src/ics except for BoundingBoxIC which is found in moose/framework/src/ics.
BoundingBoxIC

BoundingBoxIC
BoundingBoxIC allows setting the initial condition of a value inside and outside of a specified box. The box is aligned with the x,y,z axis, and is specified by passing in the x,y,z coordinates of the bottom left point and the top right point. Each of the coordinates of the "bottom_left" point MUST be less than those coordinates in the "top_right" point. When setting the initial condition if bottom_left <= Point <= top_right then the inside value is used. Otherwise the outside value is used. More information can be found on the BoundingBoxIC syntax page.
Inputs
x1: The x coordinate of the lower left-hand corner of the boxy1: The y coordinate of the lower left-hand corner of the boxz1: The z coordinate of the lower left-hand corner of the boxx2: The x coordinate of the upper right-hand corner of the boxy2: The y coordinate of the upper right-hand corner of the boxz2: The z coordinate of the upper right-hand corner of the boxinside: The value of the variable inside the boxoutside: The value of the variable outside the box
RndBoundingBoxIC

RndBoundingBoxIC
Like BoundingBoxIC but the inside and outside values are randomly chosen from a uniform distribution between the mx_invalue and mn_invalue inside the box and mx_outvalue and mn_outvalue outside the box. More information can be found on the RndBoundingBoxIC syntax page.
Inputs
x1: The x coordinate of the lower left-hand corner of the boxy1: The y coordinate of the lower left-hand corner of the boxz1: The z coordinate of the lower left-hand corner of the boxx2: The x coordinate of the upper right-hand corner of the boxy2: The y coordinate of the upper right-hand corner of the boxz2: The z coordinate of the upper right-hand corner of the boxmx_inside: The max value of the variable inside the boxmn_inside: The min value of the variable inside the boxmx_outside: The max value of the variable outside the boxmn_outside: The min value of the variable outside the box
SmoothCircleIC
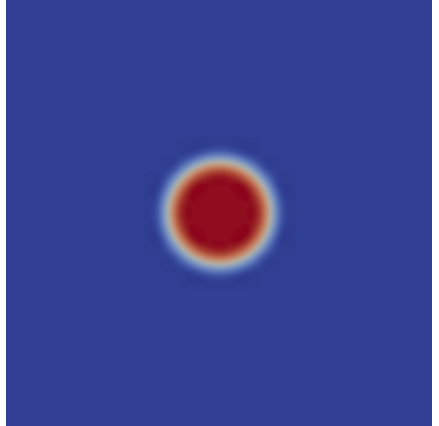
SmoothCIrcleIC
SmoothcircleIC creates a circle of a given radius centered at a given point in the domain. If int_width > zero, the border of the circle with smoothly transition from the invalue to the outvalue. More information can be found on the SmoothCircleIC syntax page.
Inputs
x1: The x coordinate of the circle centery1: The y coordinate of the circle centerz1: The z coordinate of the circle center, defaults to 0.radius: The radius of the circleinvalue: The variable value inside the circleoutvalue: The variable value outside the circleint_width: The interfacial width of the void surface. Defaults to 0.3D_spheres: In 3D, whether the objects are spheres or columns, defaults totrue
RndSmoothCircleIC
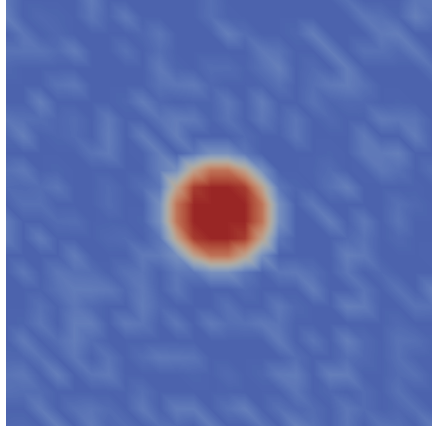
RndSmoothCircleIC
Same as SmoothCircleIC but the value inside the circle randomly around invalue by plus or minus variation_invalue and the value outside the circle randomly varies around outvalue by plus or minus variation_outvalue. More information can be found on the RndSmoothCircleIC syntax page.
Inputs
x1: The x coordinate of the circle centery1: The y coordinate of the circle centerz1: The z coordinate of the circle center, defaults to 0.radius: The radius of the circleinvalue: The variable value inside the circleoutvalue: The variable value outside the circleint_width: The interfacial width of the void surface. Defaults to 0.variation_invalue: Plus or minus this amount on the invaluevariation_outvalue: Plus or minus this amount on the outvaluerand_seed: Seed value for the random number generator, defaults to 12345.
MultiSmoothCircleIC
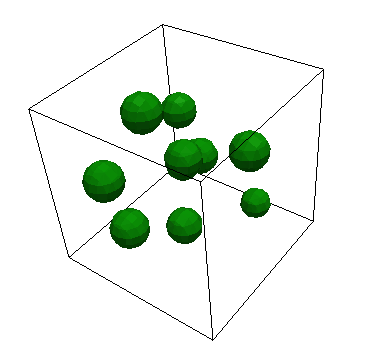
MultiSmoothCircleIC
MultiSmoothcircleIC sets variable values by creating nbub number of circles with center points randomly positioned throughout the domain. The value within a circle is invalue and outside is outvalue. More information can be found on the MultiSmoothCircleIC syntax page.
Inputs
radius: The radius of the circleinvalue: The variable value inside the circleoutvalue: The variable value outside the circleint_width: The interfacial width of the void surface. Defaults to 0.3D_spheres: In 3D, whether the objects are spheres or columns, defaults totruenumbub: The number of bubbles to be placed on GBbubspac: Minimum spacing of bubbles, measured from center to centernumtries: The number of tries allowed to fit a circle within the domain before throwing an error, defaults to 1000.Lx: Length of simulation domain in x-directionLy: Length of simulation domain in y-directionLz: Length of simulation domain in z-direction, defaults to 0rand_seed: Seed for the random number generator, defaults to 2000radius_variation: Plus or minus fraction of random variation in the bubble radius, defaults to 0
LatticeSmoothCircleIC
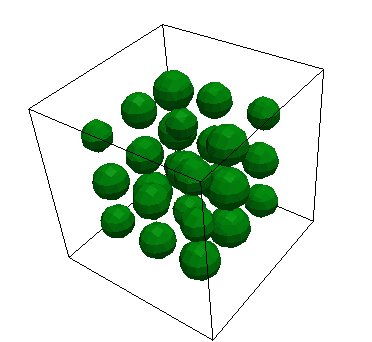
LatticeSmoothCircleIC
LatticeSmoothcircleIC sets variable values using a set of smooth circles (see SmoothCircleIC) with centers on a uniform lattice, randomly perturbed from the lattice. The value within a circle is invalue and outside is outvalue. More information can be found on the LatticeSmoothCircleIC syntax page.
Inputs
radius: The radius of the circleinvalue: The variable value inside the circleoutvalue: The variable value outside the circleint_width: The interfacial width of the void surface. Defaults to 0.3D_spheres: In 3D, whether the objects are spheres or columns, defaults totrueRnd_variation: Percent variation (plus or minus) from circle center location on the lattice.circles_per_side: Length 3 vector containing the number of bubbles along each side (x, y, and z).Lx: Length of simulation domain in x-directionLy: Length of simulation domain in y-directionLz: Length of simulation domain in z-direction, defaults to 0rand_seed: Seed for the random number generator, defaults to 2000radius_variation:Plus or minus fraction of random variation in the bubble radius, defaults to 0
SpecifiedSmoothCircleIC
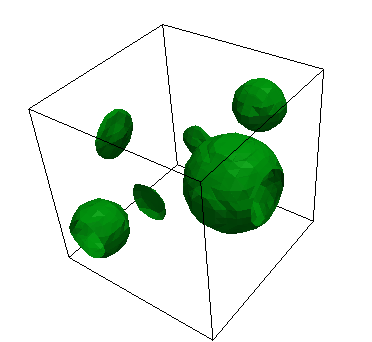
SpecifiedSmoothCircleIC
SpecifiedSmoothcircleIC creates a user specified number of smooth circles and specific locations and with specific radii. The value within a circle is invalue and outside is outvalue. More information can be found on the SpecifiedSmoothCircleIC syntax page.
Inputs
invalue: The variable value inside the circleoutvalue: The variable value outside the circleint_width: The interfacial width of the void surface. Defaults to 0.3D_spheres: In 3D, whether the objects are spheres or columns, defaults totruex_positions: A vector containing the x-coordinate for each circle centery_positions: A vector containing the y-coordinate for each circle centerz_positions: A vector containing the z-coordinate for each circle centerradii: A vector containing the radius for each circle
CrossIC
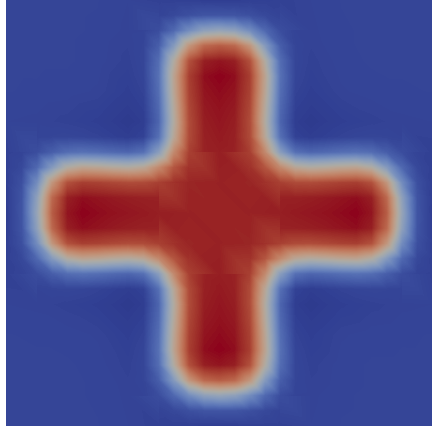

CrossIC
CrossIC is a 2D ONLY IC that sets the variable value to be average + amplitude within a smooth cross shape and to average - amplitude outside the cross. The cross is defined within a square defined by the user. More information can be found on the CrossIC syntax page
Input
x1: The x coordinate of the lower left-hand corner of the boxy1: The y coordinate of the lower left-hand corner of the boxx2: The x coordinate of the upper right-hand corner of the boxy2: The y coordinate of the upper right-hand corner of the boxaverage: The average variable value within the domain, defaults to 0amplitude: The variation from the average within the cross (average+amplitude) and outside of the cross (average-amplitude).
ThumbIC
Thumb shaped bicrystal for grain boundary mobility tests. More information can be found on the ThumbIC syntax page.
PolycrystalICs
PolycrystalICs are described here.